Typescript, explained.
What is TypeScript? You've heard about it as the perfect companion to Javascript. But what is it and how does it work?
Let's explain!
Take a look at this Javascript code:
var number1 = 5
var number2 = 10
var sum = number1 + number2
console.log(sum)
What is the output of the code?
If your answer is 15 then you're right! You have two numbers, number1 and number2. If you add them together using the + sign, it will give you the total because they're both numbers!
Now take a look at this:
var number1 = "5"
var number2 = "10"
var sum = number1 + number2
console.log(sum)
This time number1 and number2 are strings. So what will this code give as output?
If your answer is "510" as a string, then you're right again!
But that's not how you expect it to work.
I want number1, number2, and sum to all be numbers so that sum gives me the actual sum every time.
Wouldn't it be nice if we could put some rules in so that we're absolutely CERTAIN that number1, number2 and sum are ALWAYS numbers?
Let's look at another example:
Suppose, this time, we want to divide two numbers together:
var number1 = 10
var number2 = 2
var result = number1 / number2
console.log(result)
The result of the above is (as you'd expect), 5. But what if instead of a number, number2 is a string, or an array?
var number1 = 10
var number2 = []
var result = number1 / number2
console.log(result)
What would you expect it to happen here?
If your answer is "it would give me an error" then you'd be wrong. The result would be "Infinity". But that is non-sense!
There should be some rule in place that says "you can only divide numbers with numbers". Wouldn't that be nice?
Enter TypeScript!

TypeScript is a language that is basically extended Javascript.
In essence, TypeScript allows you to write Javascript so that when you declare variables or functions, you can also specify what type each of them are (string, number, array etc).
For example:
"I want to create a variable called total which is a number":
var total:number = 5
"I want to create a variable name which is a string":
var name:string = "Savvas"
"I want to create a function getTotal which should always get a number array as input and always return a number":
function getTotal(values:number[]):number{
return values.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => {
accumulator + currentValue
})
}
So what would happen if I write a string in the total variable in my TypeScript (.ts) file, since it expects a number?
var total:number = "ABC"
This:
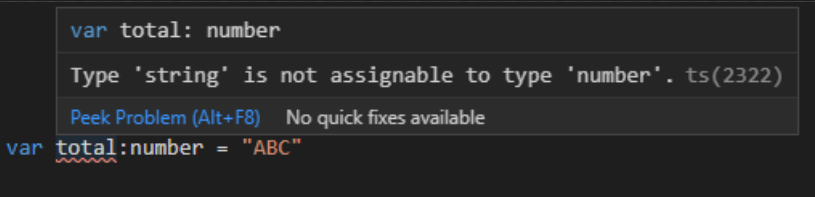
This is what's so amazing about TypeScript. It tells you that what you're assigning is wrong before you even hit save! That means this error never makes it to your users, and it makes fixing errors a lot LOT easier!
So how do I get started?
You can install TypeScript using via NPM:
npm install -g typescript
You can then turn a TypeScript (.ts) file into a Javascript (.js) file by running this command:
npx tsc myfile.ts
You can then attach your JS file to your HTML as normal!
This thread only touches the absolute basics of TypeScript but you can learn a lot more on the TypeScript official documentation which is quite comprehensive!
Enjoy!
Dev, Explained (43 part series)
- Javascript Scopes, explained.
- Javascript Promises, explained.
- Accessibility, explained.
- React, explained
- Should I use forEach() or map()?
- Should I use Flexbox or CSS Grid?
- Docker, explained.
- Unit testing, explained
- Git, explained.
- Typescript, explained.
- async/await, explained.
- The DOM, explained.
- Regular expressions, explained
- GraphQL, explained.
- Vue, explained.
- Svelte, explained.
- API, explained.
- Javascript Hoisting, explained.
- Immediately Invoked Function Expressions (IIFE), explained.
- ARIA roles, explained.
- Test-driven Development, explained.
- ARIA live regions, explained.
- aria-label in accessibility, explained.
- Type coercion in Javascript, explained.
- Variables, explained.
- if statements, explained.
- Arrays, explained.
- Currying in Javascript, explained.
- Memoization, explained.
- For loops, explained.
- Javascript Prototypes, explained.
- React Hooks, explained.
- Graph databases, explained.
- MongoDB, explained.
- Serverless, explained.
- Javascript Callback functions, explained.
- HTML, explained.
- CSS, explained.
- Responsive design, explained.
- Javascript, explained.
- The CSS Box Model, explained.
- CSS Flexbox, explained.
- CSS Grid, explained.
